Many Americans are poorly informed about basic constitutional provisions, according to a new national survey by the Annenberg Public Policy Center.
The annual Annenberg Constitution Day Civics Survey finds that:
- More than half of Americans (53 percent) incorrectly think it is accurate to say that immigrants who are here illegally do not have any rights under the U.S. Constitution;
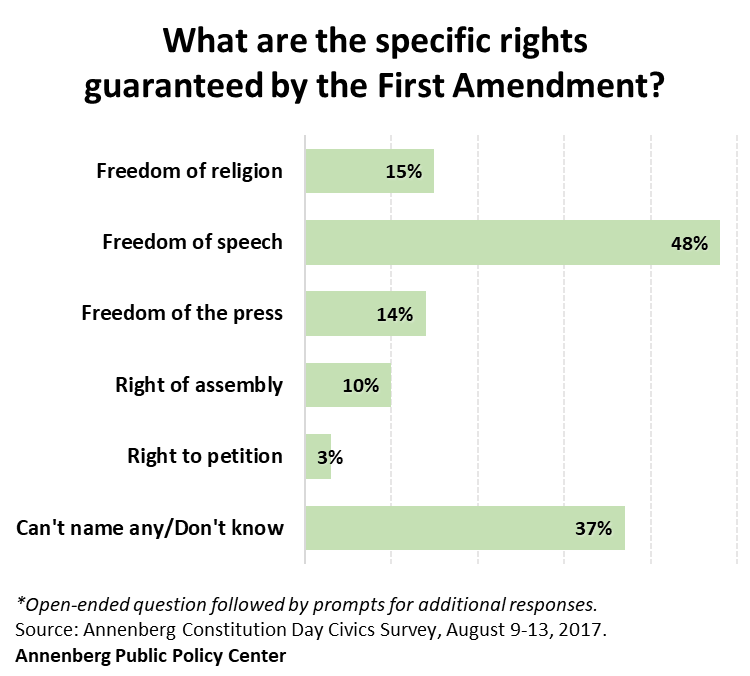
- More than a third of those surveyed (37 percent) can’t name any of the rights guaranteed under the First Amendment;
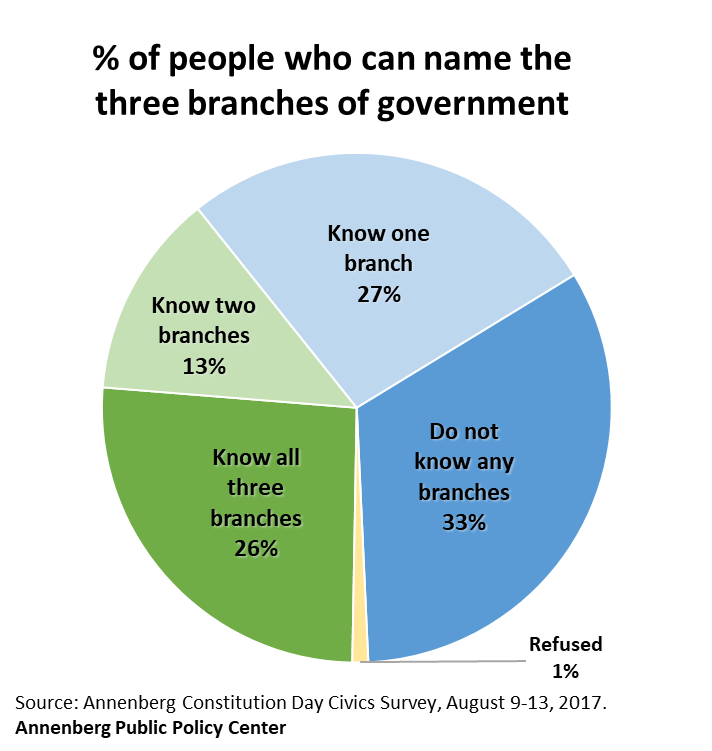
- Only a quarter of Americans (26 percent) can name all three branches of government.
[There are more up-to-date findings from this annual survey. See this page for the most recent findings.]
“Protecting the rights guaranteed by the Constitution presupposes that we know what they are. The fact that many don’t is worrisome,” said Kathleen Hall Jamieson, director of the Annenberg Public Policy Center (APPC) of the University of Pennsylvania. “These results emphasize the need for high-quality civics education in the schools and for press reporting that underscores the existence of constitutional protections.”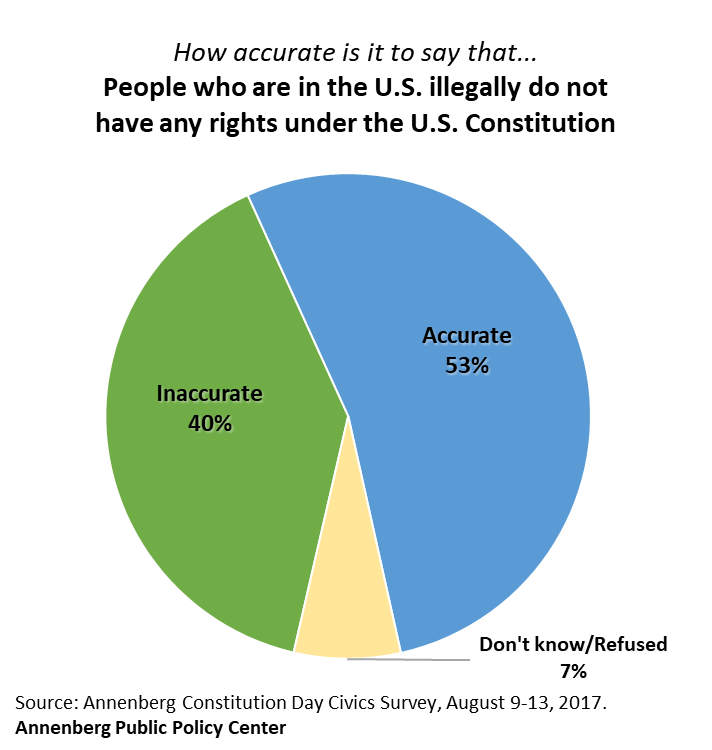
Illegal immigration and constitutional rights
The APPC survey, conducted Aug. 9-13 among 1,013 adults in the United States, finds that 53 percent think that people who are here illegally do not have any rights under the Constitution. That incorrect belief is especially strong among self-identified political conservatives – 67 percent think it is accurate, compared with 48 percent of moderates and 46 percent of liberals.
[The civics survey drew attention from national and local media and many sides of the political spectrum. Read about the coverage here.]
In fact, immigrants who are in the United States illegally share some constitutional protections with U.S. citizens. More than a century ago, in Yick Wo v. Hopkins (1886), a case involving a Chinese immigrant, the Supreme Court ruled that non-citizens were entitled to due process rights under the 14th Amendment’s equal protection clause. Other cases have expanded upon those rights.* (For more on Yick Wo, see this video on Annenberg Classroom’s website.)
Most respondents, though not all, know that under the Constitution, U.S. citizens who are atheists or Muslim have the same rights as all other citizens. Seventy-nine percent of respondents know it is accurate to say that U.S. citizens who are atheists have the same rights as other citizens, and 76 percent know it is accurate to say that citizens who are Muslim have the same rights as other citizens.
 What does the First Amendment say?
What does the First Amendment say?
Nearly half of those surveyed (48 percent) say that freedom of speech is a right guaranteed by the First Amendment. But, unprompted, 37 percent could not name any First Amendment rights. And far fewer people could name the other First Amendment rights: 15 percent of respondents say freedom of religion; 14 percent say freedom of the press; 10 percent say the right of assembly; and only 3 percent say the right to petition the government.
The First Amendment reads:
Congress shall make no law respecting an establishment of religion, or prohibiting the free exercise thereof; or abridging the freedom of speech, or of the press; or the right of the people peaceably to assemble, and to petition the Government for a redress of grievances.
Contrary to the First Amendment, 39 percent of Americans support allowing Congress to stop the news media from reporting on any issue of national security without government approval. That was essentially unchanged from last year. But the survey, which followed a year of attacks on the news media, found less opposition to prior restraint (49 percent) than in 2016 (55 percent).
 Many don’t know the branches of government
Many don’t know the branches of government
Only 26 percent of respondents can name the three branches of government (executive, judicial, and legislative), the same result as last year. In the presence of controls, people who identified themselves as conservatives were significantly more likely to name all three branches correctly than liberals and moderates. The 26 percent total was down significantly from APPC’s first survey on this question, in 2011, when 38 percent could name all three.
In the current survey, 33 percent could not name any of the three branches, the same as in 2011.
The phone survey, conducted for APPC by the research firm SSRS, has a margin of error of ±3.7 percent. For more on the methodology and questions click here.
Constitution Day and the Civics Renewal Network
APPC’s Annenberg Classroom, presented by the Leonore Annenberg Institute for Civics, has created a series of free, award-winning videos for educators and the public, including Yick Wo and the Equal Protection Clause, The Role of the Courts, and Freedom of the Press: New York Times v. United States.
Annenberg Classroom has joined with 30 other nonpartisan organizations to create the Civics Renewal Network, which offers free, high-quality educational materials online. Among CRN’s partners are the Library of Congress, the National Archives, the National Constitution Center, the U.S. Courts, the NEH’s EDSITEment Project and iCivics.
Constitution Day (Sept. 17) will be celebrated Monday, Sept. 18. To mark it, the U.S. Courts are holding naturalization ceremonies nationwide and educators will lead students in the “Preamble Challenge,” celebrating the Preamble to the Constitution.
Updated 9/15/17: An earlier version of this release incorrectly referred to the immigrant Yick Wo as undocumented.
* In Plyler v. Doe (1982), for example, the Supreme Court ruled that a Texas law violated the equal protection clause by denying a public school education to undocumented children. The Court held: “The illegal aliens who are plaintiffs in these cases challenging the statute may claim the benefit of the Equal Protection Clause, which provides that no State shall ‘deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal protection of the laws.’ Whatever his status under the immigration laws, an alien is a ‘person’ in any ordinary sense of that term.” The majority also wrote: “In addition to the pivotal role of education in sustaining our political and cultural heritage, denial of education to some isolated group of children poses an affront to one of the goals of the Equal Protection Clause: the abolition of governmental barriers presenting unreasonable obstacles to advancement on the basis of individual merit.”
Download this news release here.


