Introduction
Graduated driver licensing laws (GDL) are the national strategy to address young driver motor vehicle crashes, which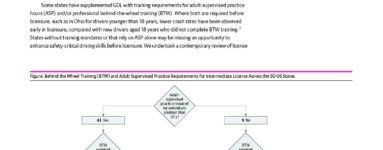 are a leading cause of injuryand mortality for US teens. The basic tenets of GDL are to delay full licensure until older ages and impose driving restrictions under the intermediate license. However, despite GDL, crash rates remain high. Prior studies have quantified that the majority (75%) of young novice driver crashes are due to driver errors, particularly related to detecting and responding to hazards. Interventions that aim to improve these crash avoidance skills before licensure should help address this preventable public health crisis.
are a leading cause of injuryand mortality for US teens. The basic tenets of GDL are to delay full licensure until older ages and impose driving restrictions under the intermediate license. However, despite GDL, crash rates remain high. Prior studies have quantified that the majority (75%) of young novice driver crashes are due to driver errors, particularly related to detecting and responding to hazards. Interventions that aim to improve these crash avoidance skills before licensure should help address this preventable public health crisis.
Some states have supplemented GDL with training requirements for adult-supervised practice hours (ASP) and/or professional behind-the-wheel training (BTW). Where both are required before licensure, such as in Ohio for drivers younger than 18 years, lower crash rates have been observed early in licensure, compared with new drivers aged 18 years who did not complete BTW training. States without training mandates or that rely on ASP alone may be missing an opportunity to enhance safety-critical driving skills before licensure. We undertook a contemporary review of license policies across the 50 states to determine BTW and ASP requirements before intermediate licensure for those younger than 18 years and whether these mandates are truly required (or can be replaced).
Authors
- Elizabeth Walshe
- Daniel Romer
- Nina Aagaard
- Flaura Winston