An analyses of ASK survey data find perceptions of scientists’ credibility remains high, but eroded somewhat from 2023 to 2024 -- and perceptions of AI scientists are lower than for scientists in general.


An analyses of ASK survey data find perceptions of scientists’ credibility remains high, but eroded somewhat from 2023 to 2024 -- and perceptions of AI scientists are lower than for scientists in general.

New paper from APPC team examined the relationship between health-related beliefs about climate change and support for climate policy proposals.

An APPC study finds more social media use correlates with more vaccination, but the reason for this is different for Democrats and Republicans.

State requirements vary widely for young driver training and a new study in JAMA Open suggests that more states should require more young driver training before granting licenses.
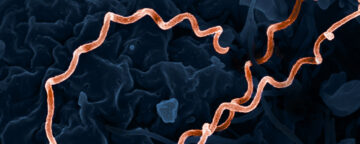
Syphilis cases are on the rise, but many Americans don’t know the symptoms, an APPC survey on sexually transmitted infections finds.

In new paper, APPC researchers probed associations between media exposure and science-consistent beliefs about climate change.

A new ASAPH survey finds that a quarter of U.S. adults do not know that claims that the MMR vaccine causes autism are false.

New survey research shows that Black Americans' knowledge about the COVID vaccine increased over time, and this increase was associated with their receipt of the vaccine.

Most Americans report having experienced the effects of extreme weather, according to a new survey that finds support for policies to lessen the effects of climate change.